Business Functions and SAP #
The Company, Definition and Objectives #
A company is a hierarchical human group that deploys intellectual, physical, and financial means to extract, transform, transport, and distribute goods or services, in accordance with objectives defined by management, involving to varying degrees the motivations of profit and social utility.
The realization of profit is an essential objective and often conditions the survival of the company.
However, the entrepreneur may have other objectives when creating their company (personal fulfillment, job creation, production of quality goods or services, environmental respect, etc.). These objectives are not incompatible with the profit objective.
A Company in SAP #
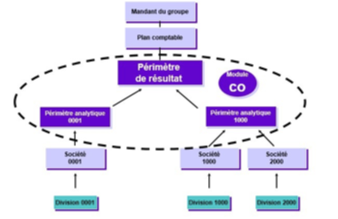
Companies in SAP are maintained in the SE16N table called T001. In this table, you can see all companies listed with their descriptions and parameters. These are configured in SPRO.
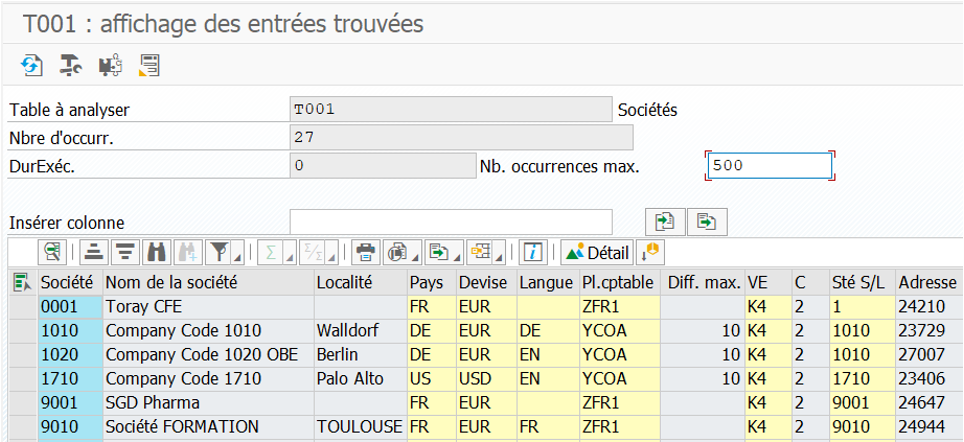
In the SPRO transaction, the company structure is defined. With the list of Company numbers and their descriptions. You can link them to a chart of accounts for the Finance module or even to an analytical scope for Management Control.
OB19 is used to link the company with the analytical scope

The Company, Its Activities #
Industrial Activity #
It buys raw materials, transforms them, and sells finished products resulting from these transformations.
For example:
Automotive Sector, Aerospace Sector, etc.
Commercial Activity (Trading) #
It buys goods and resells them in the same state (without transformation).
For example:
SOUFLET Group in grain trading.
Service Activity #
When it produces and sells services.
For example: An ESN (IT Services Company).
Distinction Between Product and Service #
A product has a material reality (it is said to be tangible): you can touch it, transport it to a distributor to make it available to the customer.
If a service, like a product, requires labor and equipment, it does not use raw materials. It is intangible.
A product can be stored, which is not the case for a service.
A company can have both industrial, commercial, and service activities.
Example: AIRBUS
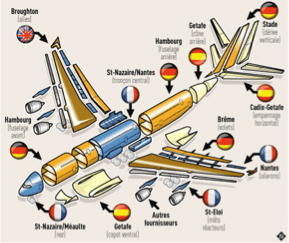
Example : Services proposed by Airbus

Articles on SAP: Product or Service? #
Products or services are distinguished by their article group. Sometimes even by their nomenclature.
Displaying an article is done in transaction MM03 and has several views: general data, sales data, customs data, accounting, or inventory.


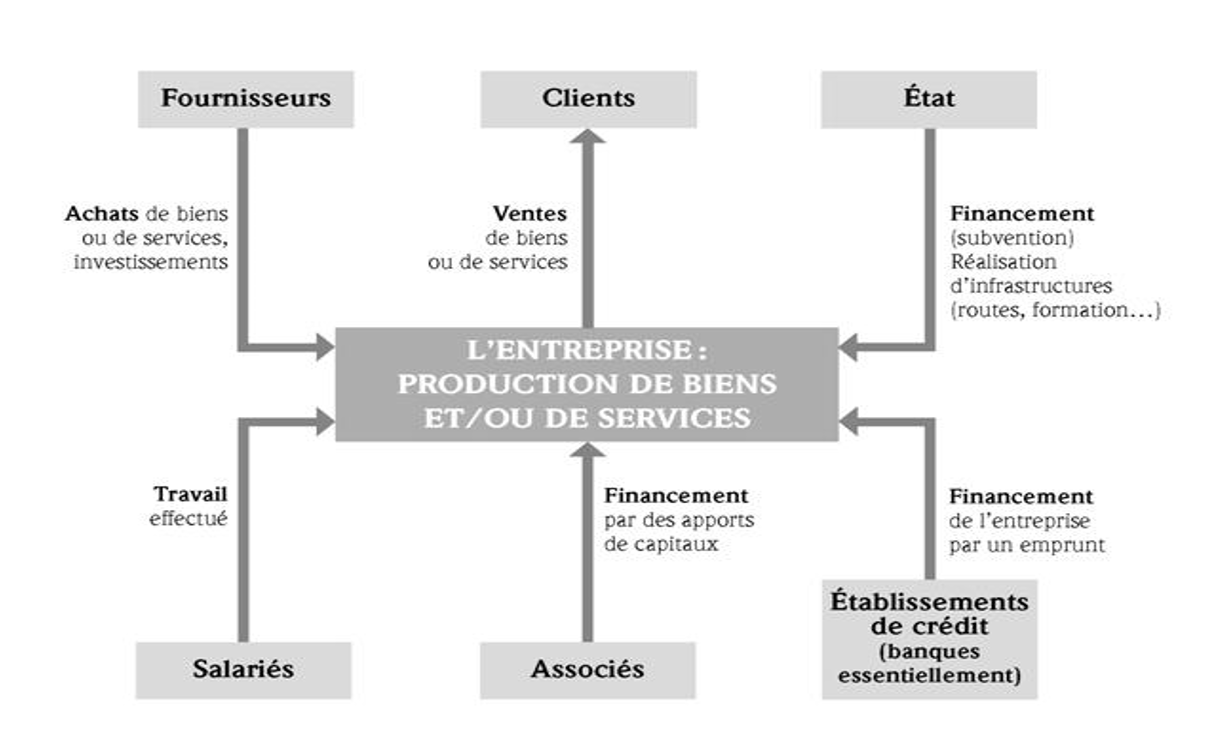
Company Partners #
Customers:
- Customers are people who buy the goods and services offered by the company. They are either individuals or companies.
Suppliers:
-
Suppliers of goods. They sell raw materials, supplies, or merchandise. They are regular partners who satisfy the company’s daily activity needs.
-
Suppliers of fixed assets. They provide the company with productive equipment and furniture. They are occasional partners who satisfy needs related to the start of activity and the renewal of worn material means.
-
Service suppliers. They can offer regular services such as transportation of finished products, as well as occasional services such as IT maintenance.
Associates:
-
These people contribute capital (money) when creating the company. This capital is useful at the start of activity for acquiring premises, machines, raw materials, merchandise, etc.
-
This financial participation gives them the right to shares that allow them to participate in decisions and, in some cases, to receive remuneration from the company’s profits.
Employees:
- They are generally composed of: managers, responsible for managing and conducting operations through the supervision of appropriate human resources; employees, responsible for executing commercial and production processes in liaison with management. They receive a salary in exchange for their work performed within the company.
Banks and Other Financial Institutions:
- They lend money to companies. They also manage their bank accounts.
The State:
- Various administrations (e.g., tax administration) and social organizations (e.g., health insurance, unemployment insurance).
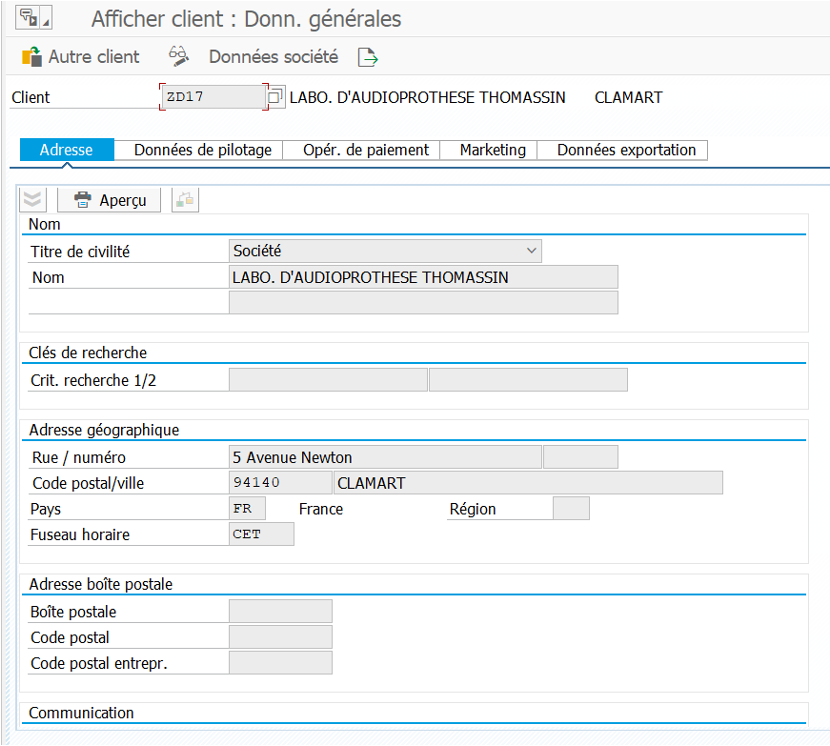
Customers and Suppliers on SAP ECC #
Customers and suppliers on SAP ECC are maintained respectively in XD03 and XK03. With company and commercial data for customers; and company data for suppliers.
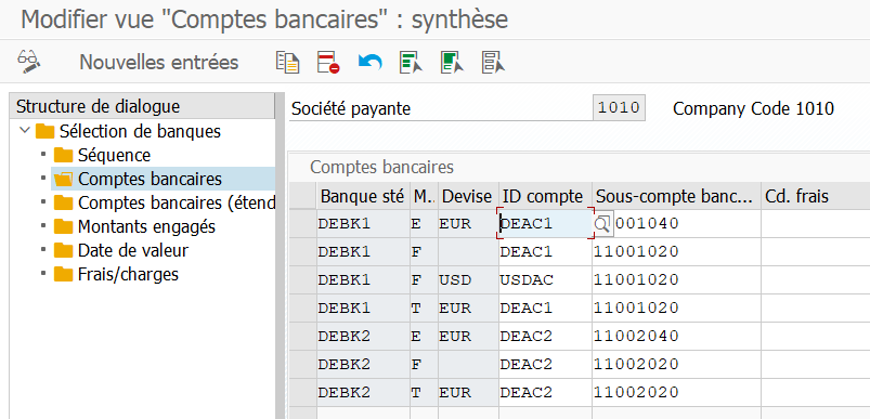
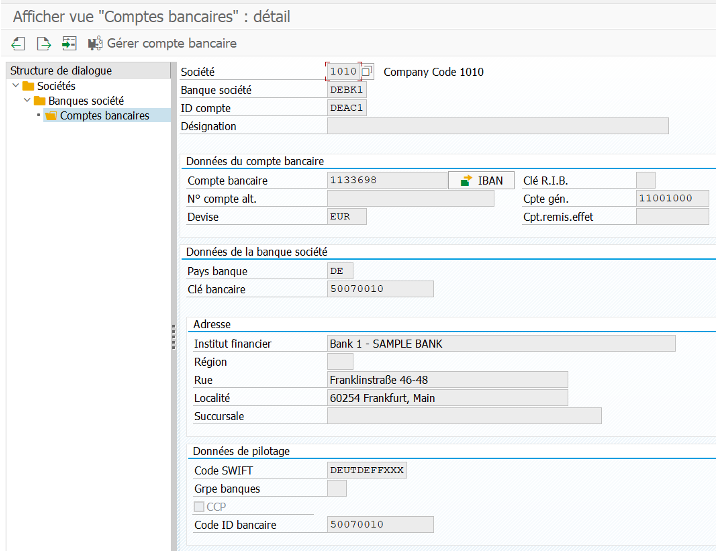
Banks on SAP #
The management of bank accounts is done via transaction FI01, FI12, and FBZP.
Exchanges Between the Company and Its Partners => Flows #
Operations between the company and its partners generate exchanges, called “flows”.
A flow is a movement of goods, services, monetary values, or information between two partners.
Different types of flows:
Information Flows:
Example: The customer sends to Airbus the type and number of goods to be delivered.
Airbus communicates to its suppliers the raw materials and services it will need to deliver the customer order.
Physical Flows:
Example: Airbus receives raw materials from its suppliers in order to produce the customer order.
Airbus delivers the goods to the customer.
Financial Flows:
Example: Airbus pays its suppliers for the ordered raw materials.
The customer pays for the planes delivered to Airbus.
SAP Modules #
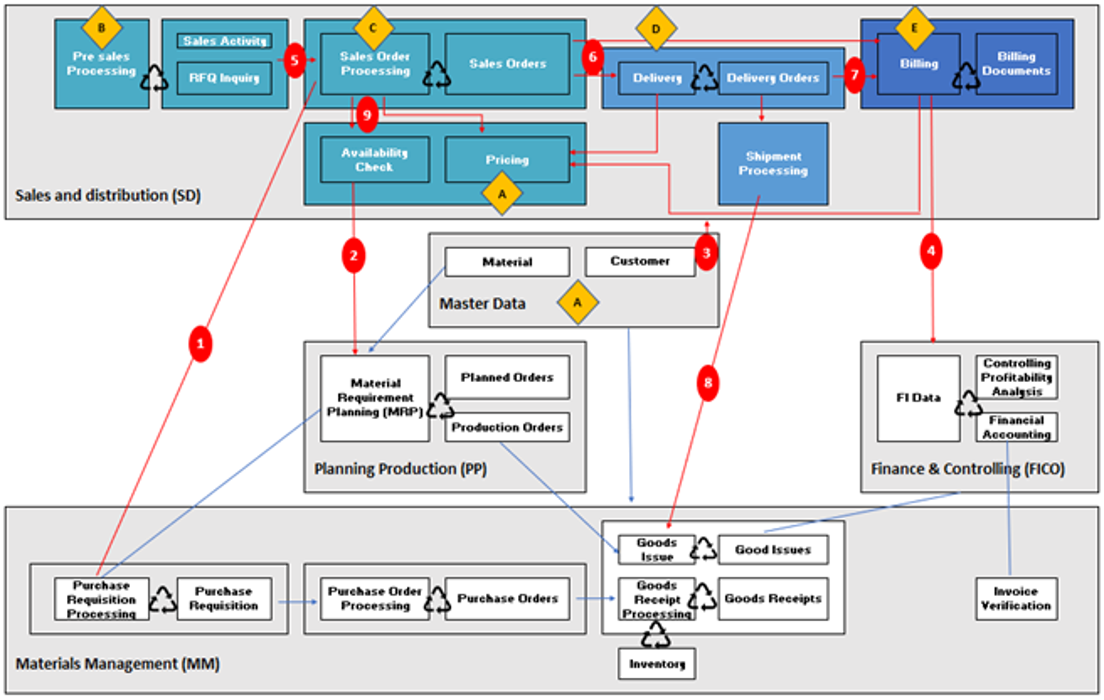
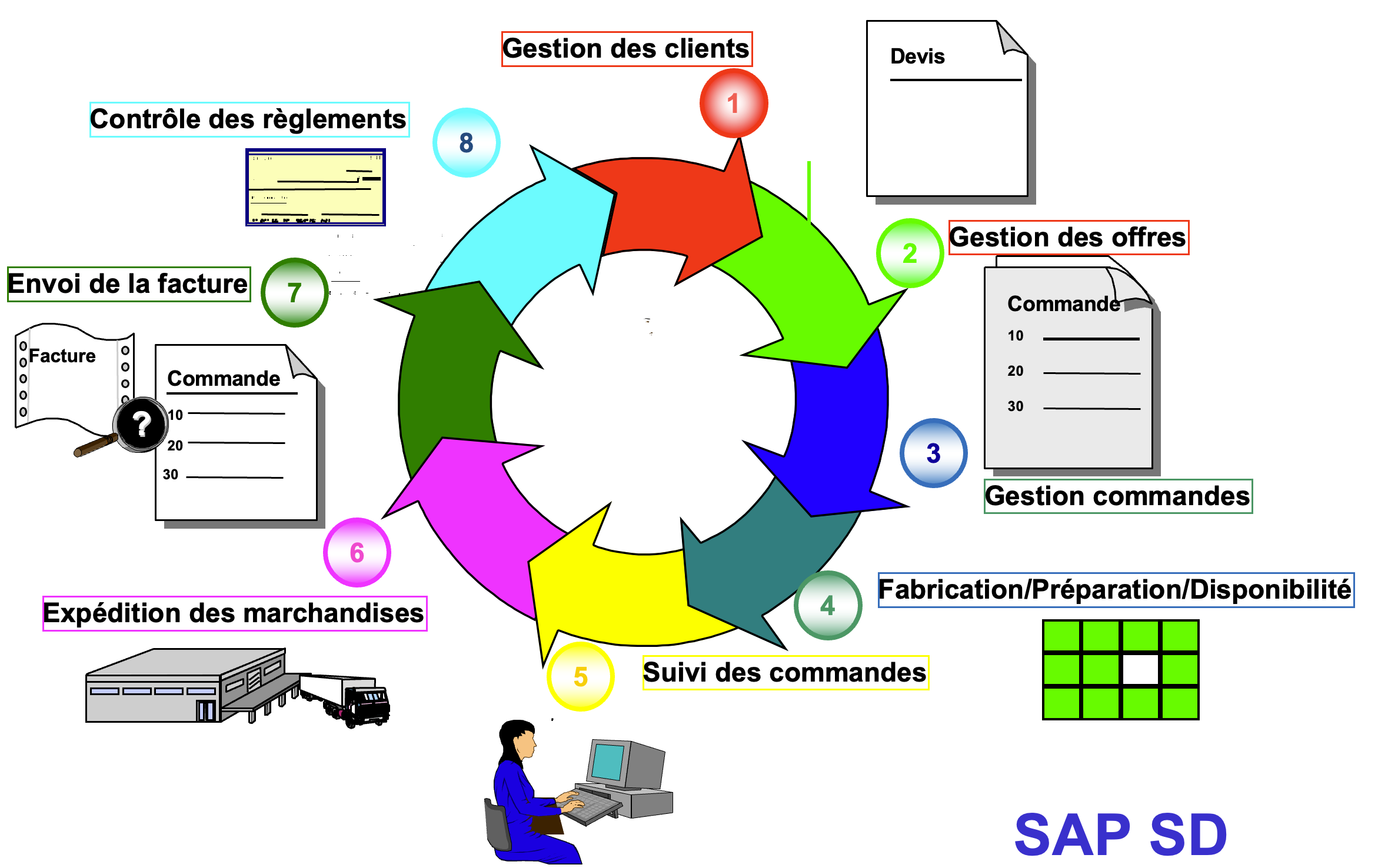
SD Flow on SAP #
It is divided into 4 main parts:
-
Sales supports: customer contacts, customer file
-
Sales: management of price quotes, framework agreements, processing of customer orders
-
Shipments: planning of preparation, execution of order preparation, goods issue, delivery note
-
Invoicing: invoice on delivery note, service invoices, credit notes
-
In this process, the Finance module manages customer payments.
SD Flow – Customer Sales Order
-
VA01 – Customer sales order
-
VL01N – Goods issue
-
VF01 - Invoicing
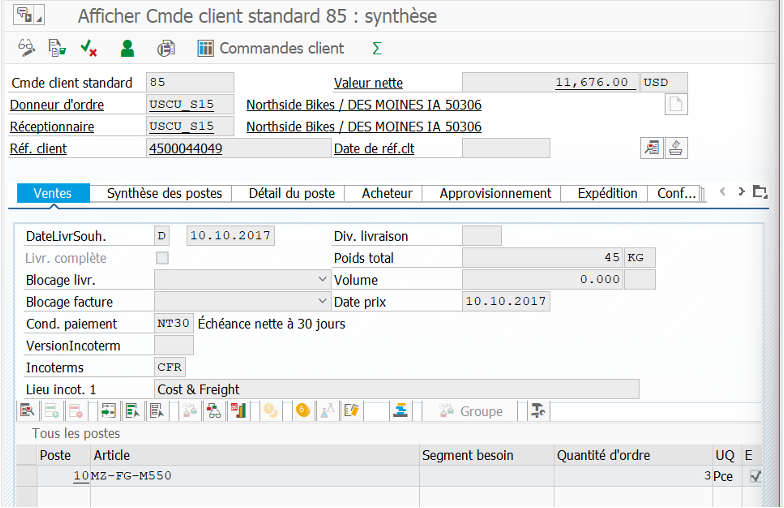
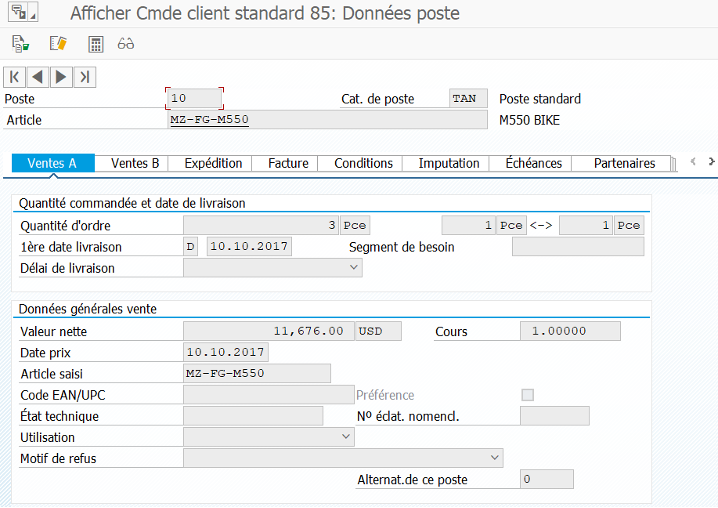
VA01 #
Creation of customer sales order
Full SD Flow #

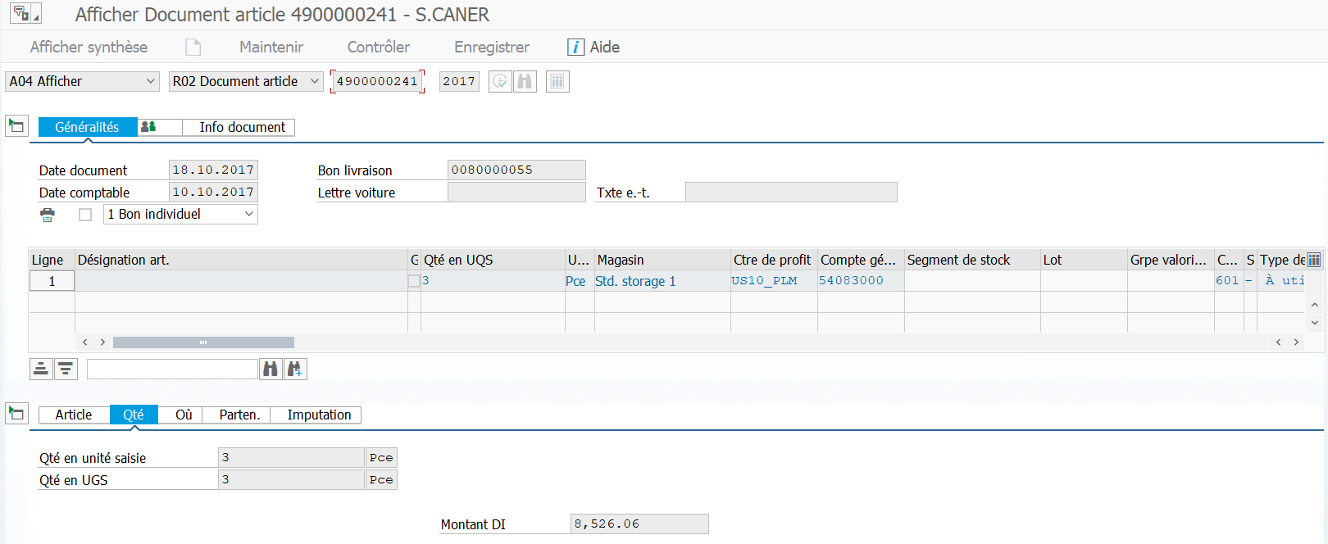
VL01N #
Creation of goods issue, delivery:
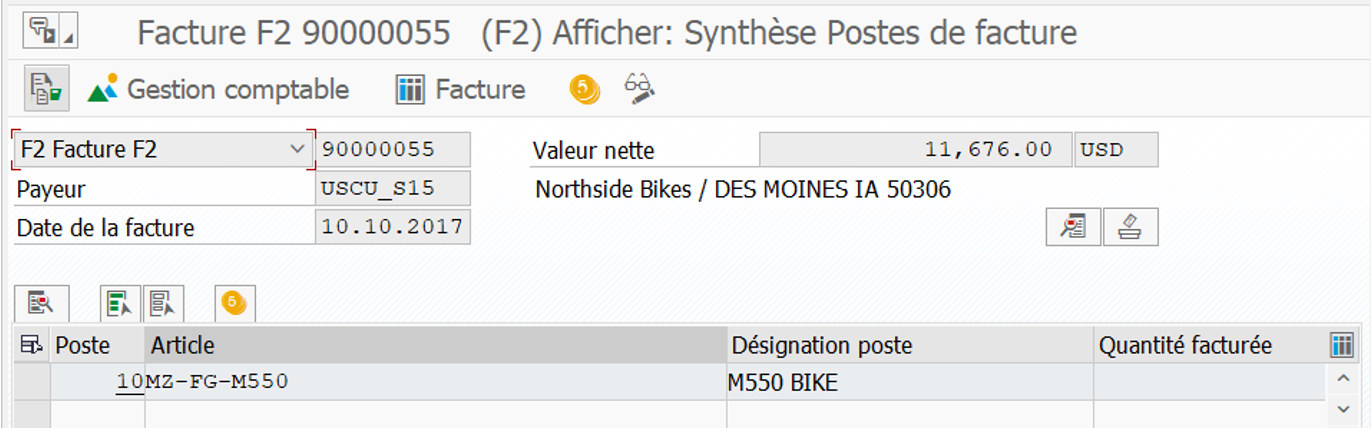
VF01 #
Invoicing of the customer order:
MM Flow on SAP #
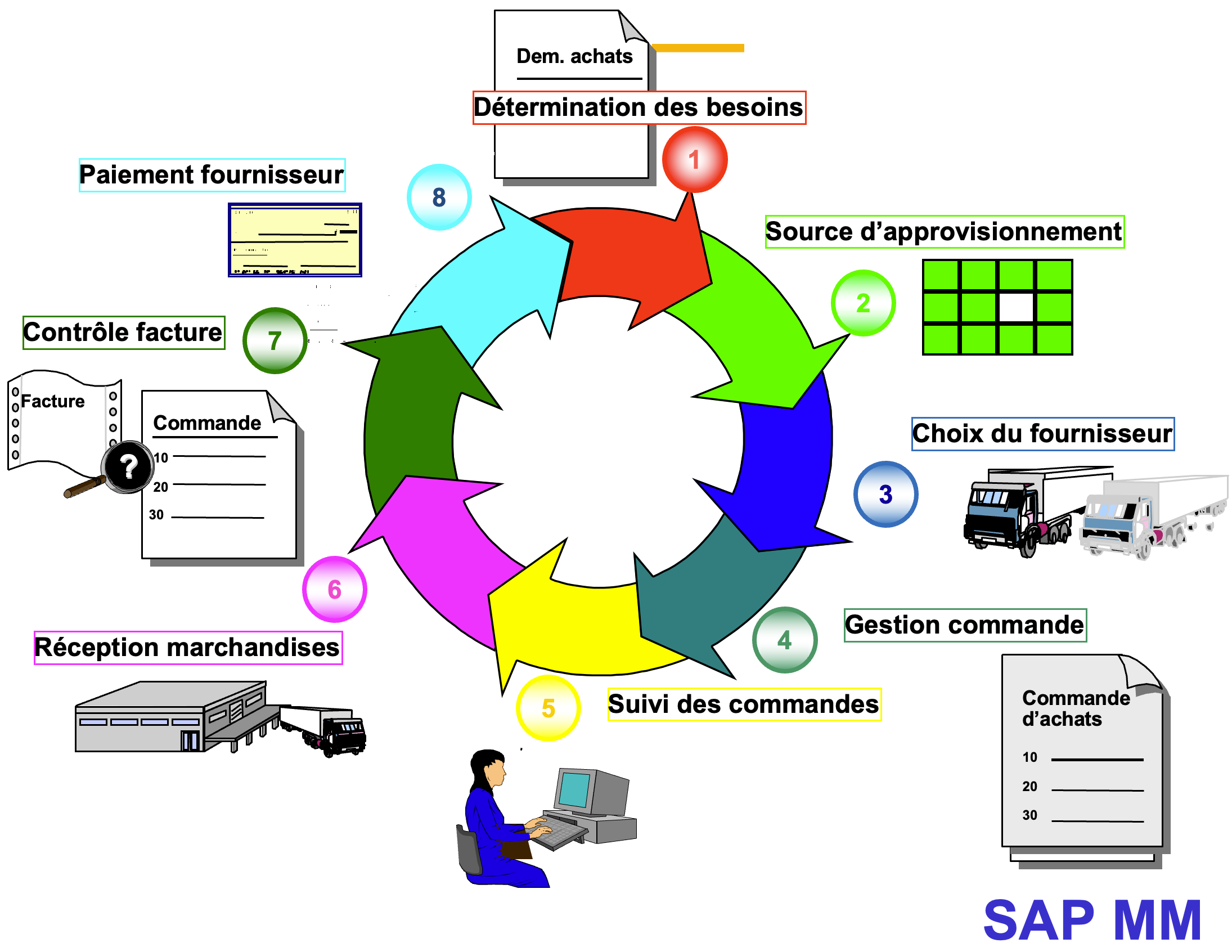
The “Purchasing” MM part has the following functionalities:
-
Demand planning
-
Supply control
-
Purchase management (ordering stocked items, ordering non-stocked products such as office supplies, printing or sending orders via EDI, price scales, supply sources)
-
Supply management (Inventory tracking, Demand analysis, In-transit tracking)
-
Invoice verification (integration with accounting)
-
Subcontracting management (Component provision, visualization of stocks at subcontracting partner locations)
-
In this process, the Finance module manages supplier payments as well as goods valuation.
MM Flow – Supplier Purchase Order
-
ME21N – Supplier purchase order
-
ME29N - Purchase order release
-
MIGO – Goods issue
-
MIRO - Invoicing
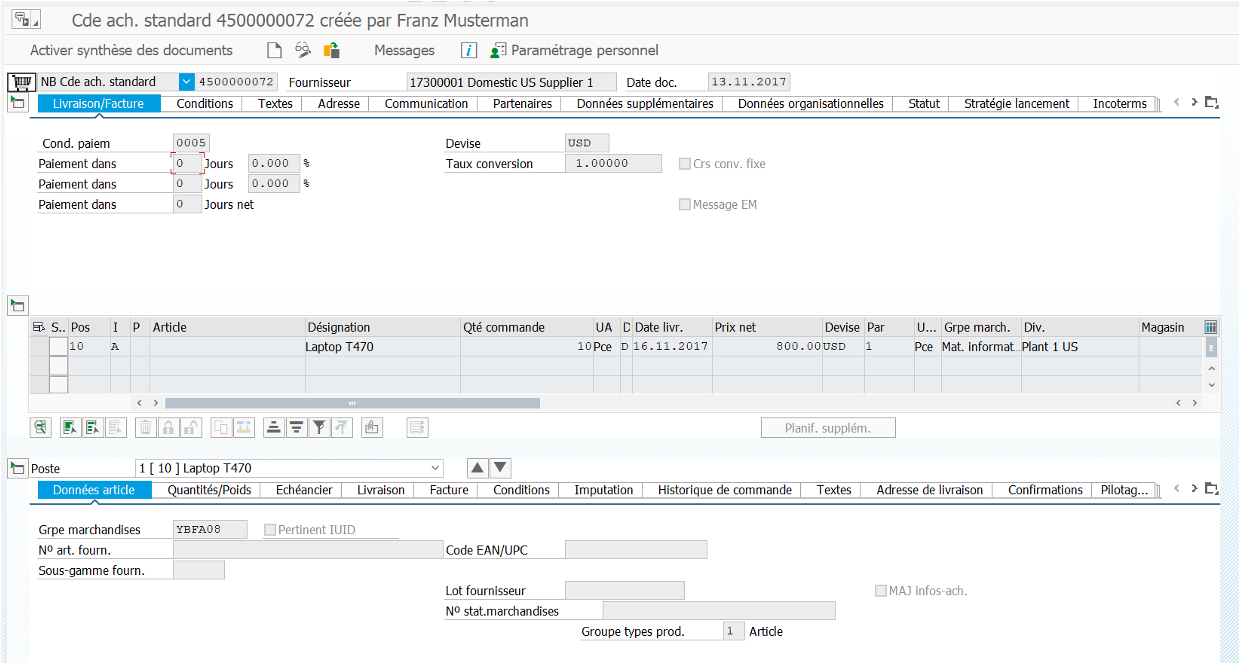
ME21N #
Creation of supplier purchase order:
Follow MM Flow #
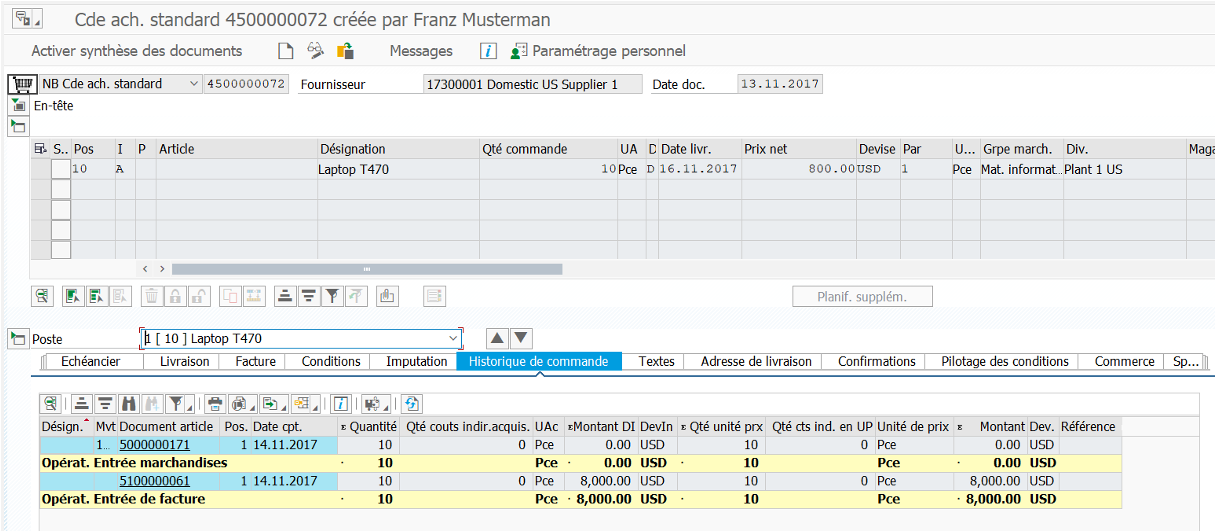
ME29N #
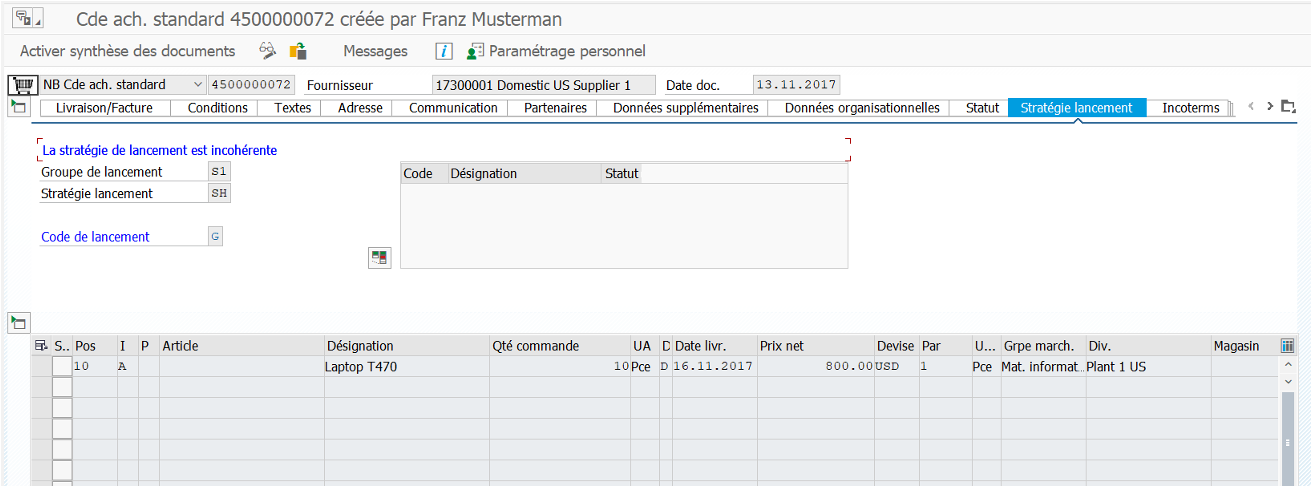
MIGO #
Goods issue:
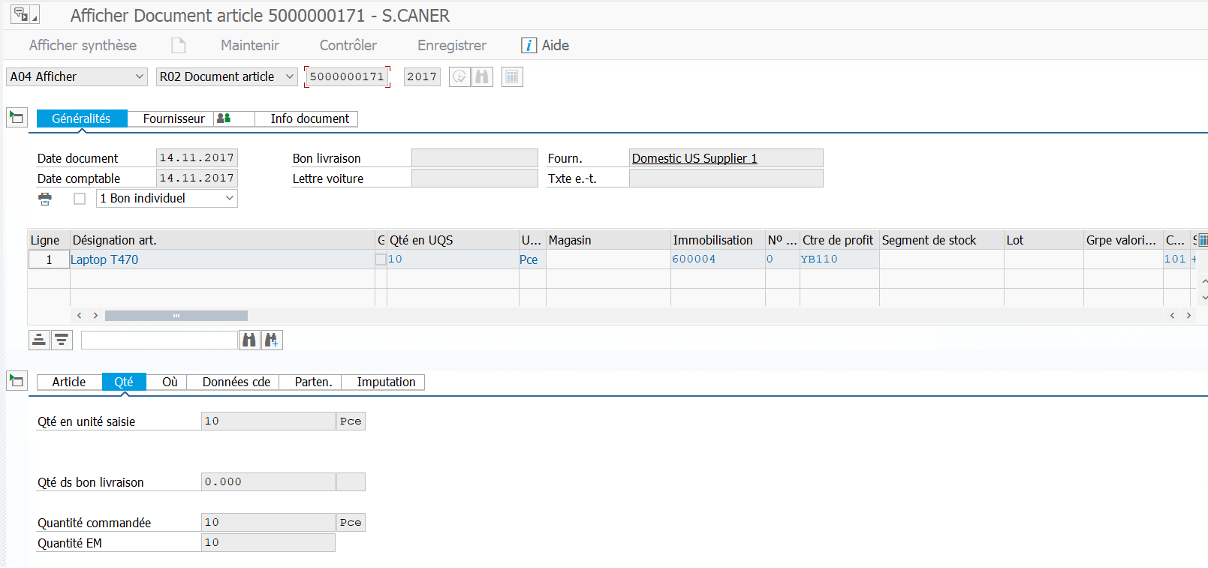
MIRO #
Invoicing of supplier purchase order:
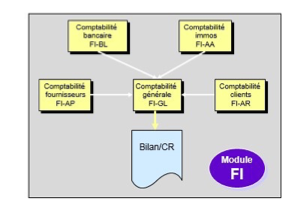
FI Flow on SAP #
The FI (Finance) module manages accounting information for external needs (legal constraints such as the preparation of balance sheet, income statement, or cash flow).
The “Financial Accounting (FI)” module complies with accounting standards and legal requirements. It allows you to generate financial statements:
-
Balance sheet
-
Income statement
-
Cash flow
-
Consolidated reserves
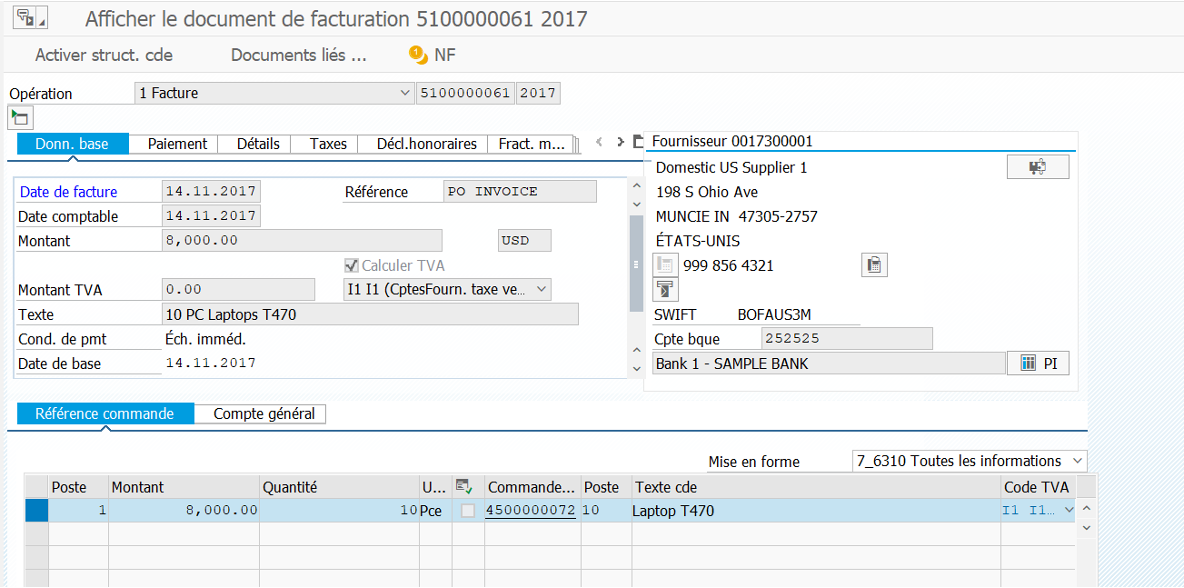
Display FI document after customer invoicing in VF01:
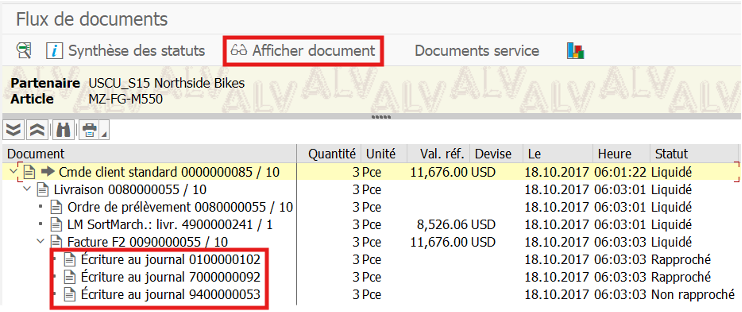
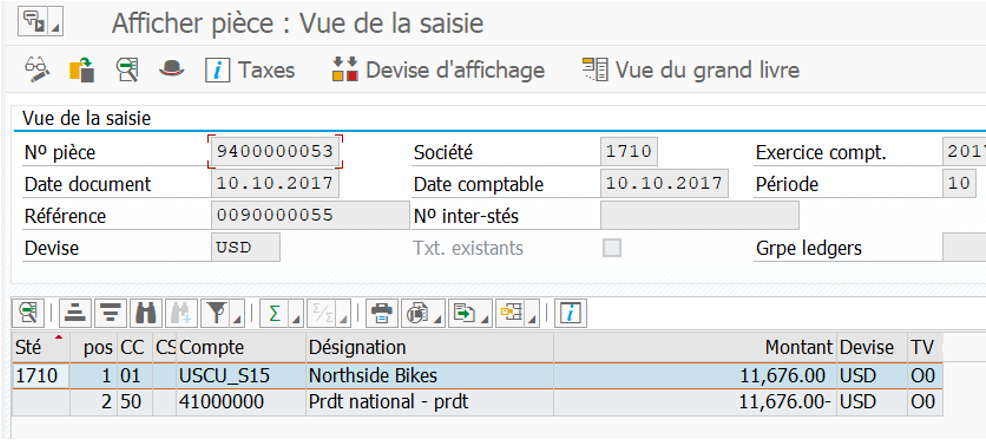
Display FI document after supplier invoicing in MIRO:
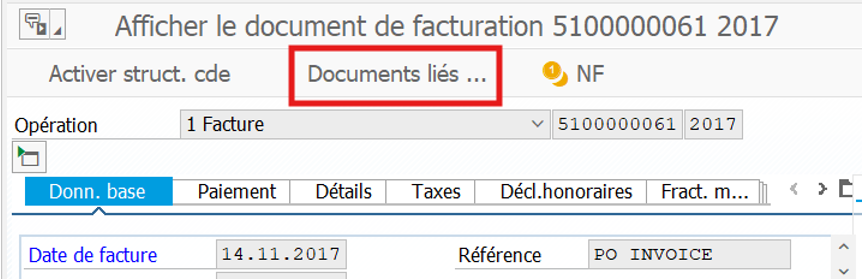
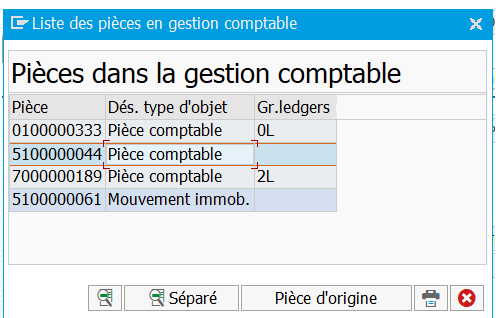
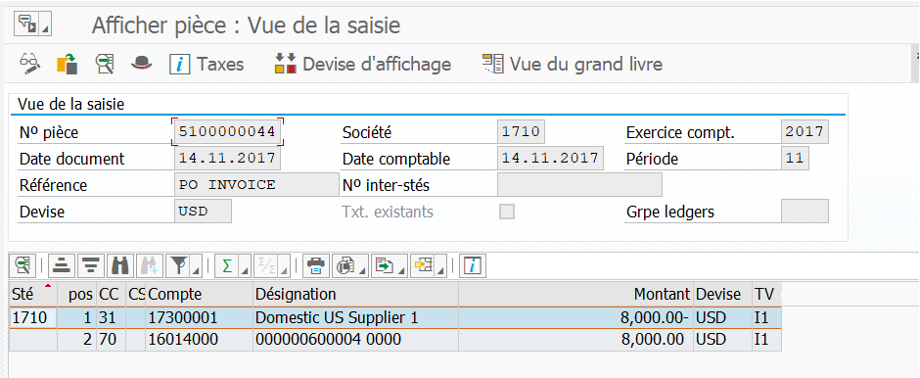
In FB03 you can see the source document whether it’s MM or SD side:
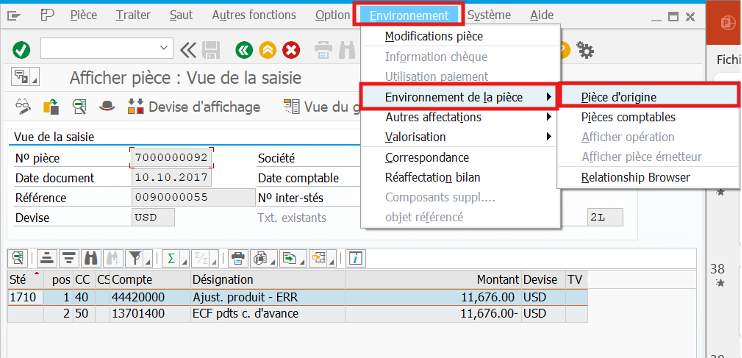
In our case, it’s an FI accounting document linked to a customer invoice.
CO Flow on SAP #
The CO (Management Control) module which allows it to internally pilot the company with “in-house” reports (Example: Profitability by product family).
The “Management Control (CO)” module provides information for management decision-making. All data relevant to the analysis is routed to the Management Control module. It allows you to generate internal and company-specific reports:
-
Cost analysis by product
-
Cost origin analysis
-
Product tracking
-
Margin statements
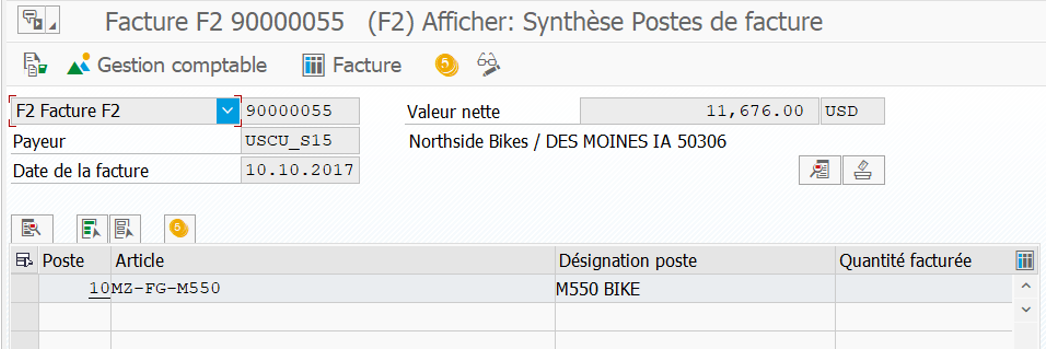
CO document in KSB5:
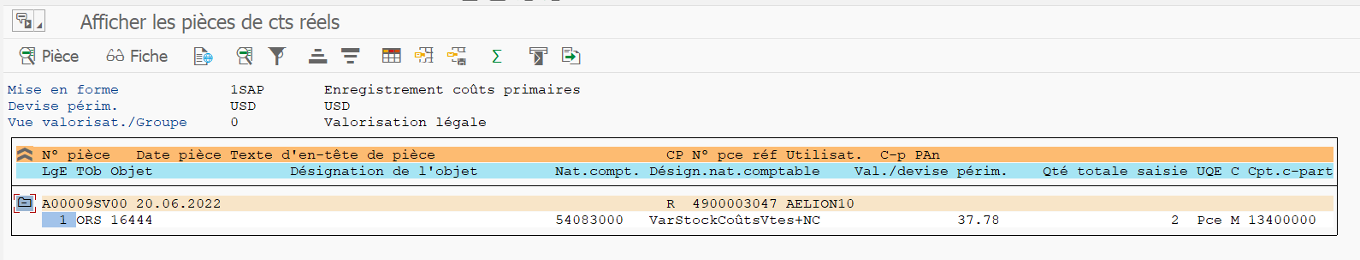
This CO document was generated following an FI document:

On the inventory variation line of this FI document, we find the result object which allows the entry on CO side.
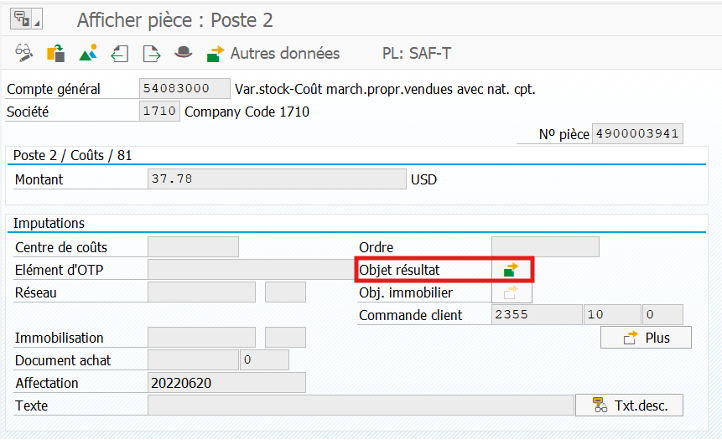

This CO entry will allow multiple CO reports to be fed in order to allow management controllers to track their costs. These reports can be adjusted according to customer needs, by adding characteristics, value components, or even adding derivations.
Report from the KE24 transaction which gives the actual individual line items of the selected result scope:

Company Functions #
A company is organized into different functions, the main ones being:
-
Management Function (Governance) whose role is to inform and decide.
-
Supply Function whose role is purchasing and storage.
-
Production Function whose role is manufacturing, quality control, etc.
-
Commercial Function whose role is sales, advertising, and market research.
-
Administrative Function whose role is accounting and financial management, personnel management, and secretarial duties.
We also speak of:
-
Operational Functions
- Set of activities and personnel directly related to the manufacturing, shipping of goods produced by the company (production, sales, logistics, etc.). Operations personnel are direct actors on the flows processed by the company.
-
Support Functions
- Usually groups activities and personnel whose role is to support production, the company’s main activity, or involvement in cross-functional projects.
The Company: Management Function #
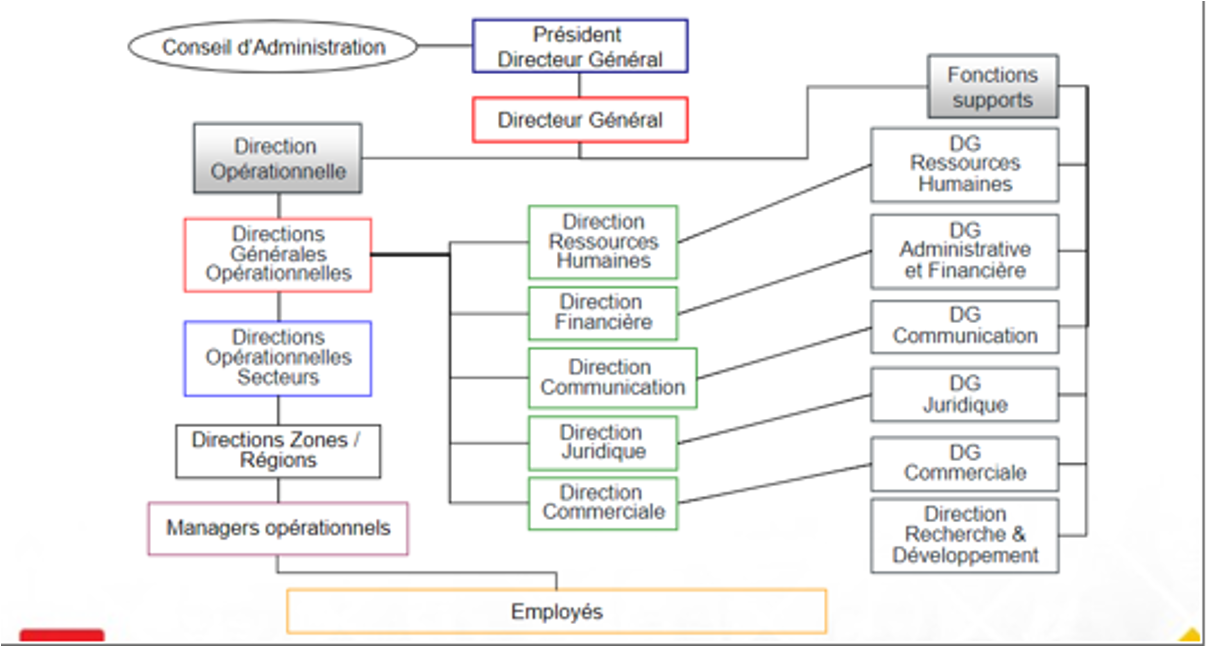
Large Enterprises and Large Groups:

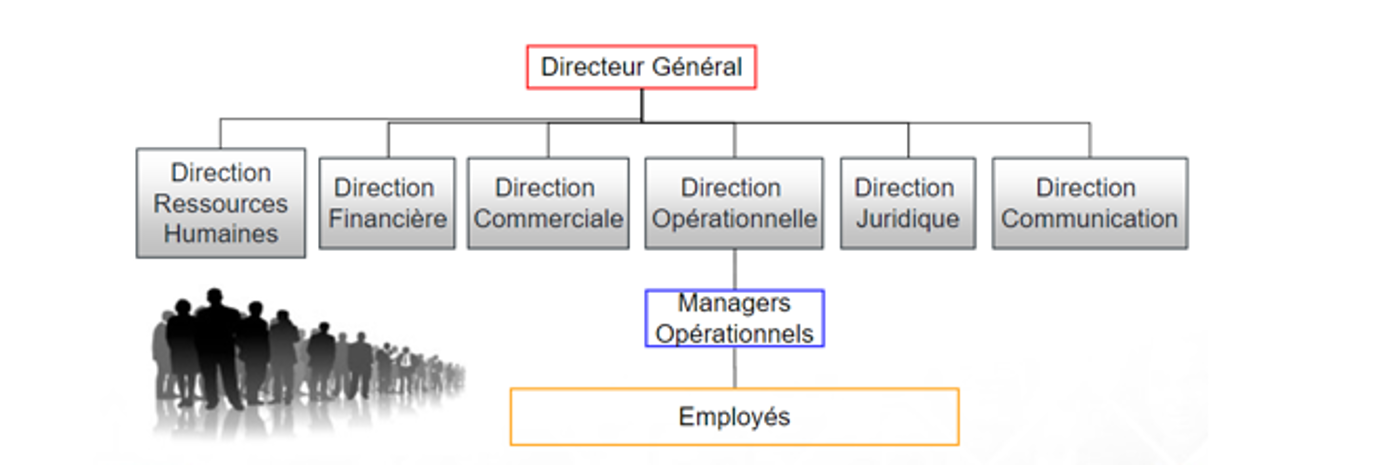
SME (Small and Medium Enterprises) or Mid-Market Enterprises:

Micro Enterprises:

The Company: Commercial Function #
The Company: Supply Function #
The Company: Production Function #
The production function (SAP PP), both because of its complexity and its importance, is divided into several departments.

